Introduction to Hot Pressing and Its Importance in Oil Extraction;
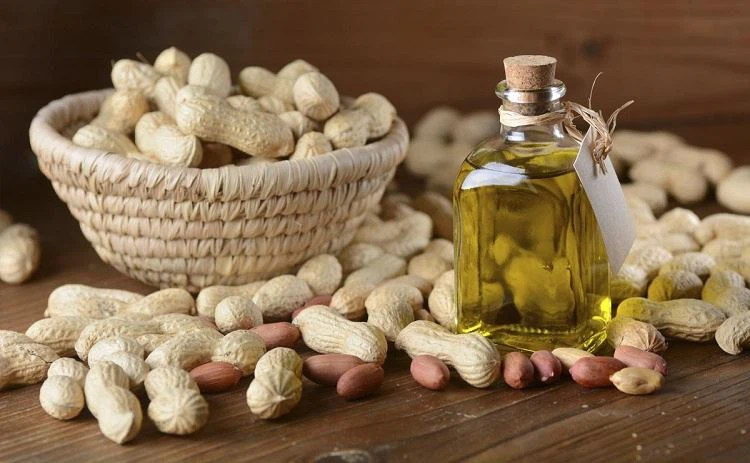
In the world of oil extraction, hot pressing stands out as a crucial method that can significantly affect oil yield. Whether you’re a farmer, food enthusiast, or curious about the science behind cooking oils, understanding this process is essential. Hot pressing involves applying heat and pressure to seeds or nuts to release their precious oils. But have you ever wondered how temperature plays into this equation? It’s not just about cranking up the heat; it’s a delicate balance between maximising yield and maintaining quality.
As we delve deeper into this topic, we’ll explore how varying temperatures influence oil extraction from common crops. From sunflower seeds to soybeans, each has its unique response to thermal conditions during processing. Join us on this journey as we unlock the secrets of hot pressing and discover what happens behind the scenes when it comes to producing some of our favourite edible oils.
Understanding the Influence of Temperature on Oil Yield;
Temperature plays a crucial role in oil extraction, particularly during the hot pressing process. As heat is applied, it affects the physical and chemical properties of oilseeds.
Higher temperatures can help break down cell walls more efficiently. This allows for easier release of oils from within the seeds. However, it’s not just about cranking up the heat; there’s a delicate balance to maintain. Excessive temperature can lead to degradation of valuable compounds within the oil. Nutrients like vitamins and antioxidants may suffer if temperatures rise too high.
Conversely, if it’s too low, you might not extract enough yield from your crops. Finding that sweet spot ensures maximum efficiency without sacrificing quality is essential for successful oil production.
Common Crops Used for Edible Oil Production;
When it comes to edible oil production, several crops take centre stage. Each offers unique flavours and nutritional profiles. The optimal edible oil hot pressing temperature typically ranges between 120°C and 160°C to ensure maximum oil yield while preserving the nutritional quality of the oil.
Soybeans are among the most popular choices globally. They yield a high amount of oil while providing essential fatty acids. Their versatility makes them a staple in many kitchens. Sunflower seeds also contribute significantly to the edible oil market. Sunflower oil is prized for its light taste and health benefits, including vitamin E content. Palm oil is another major player, especially in tropical regions. Its rich texture enhances various dishes, but raises environmental concerns due to deforestation practices associated with its cultivation.
Canola plants produce a mild-flavoured oil that’s low in saturated fat, making it favourable for health-conscious consumers. Lastly, olive trees provide one of the oldest oils known to humanity—extra virgin olive oil—celebrated for its flavour and heart-healthy properties.
Effects of Hot Pressing Temperature on Different Types of Oil Crops;
The hot pressing process is a crucial step in extracting oil from various crops. This method involves applying heat and pressure to the crop seeds, causing them to release their natural oils. However, the temperature at which this process takes place can greatly impact the final oil yield. In this section, we will explore how different hot pressing temperatures affect the extraction of oil from common crops such as sunflower, soybean, and olive.
- Sunflower seeds are widely used for their high oil content and nutritional value. When subjected to hot pressing, these seeds release oils that are rich in polyunsaturated fats and vitamin E. The optimal hot pressing temperature for sunflower seeds ranges between 90-120 degrees Celsius (194-248 degrees Fahrenheit). At lower temperatures, the oil yield may decrease due to incomplete extraction of oils from the seed. On the other hand, higher temperatures can lead to oxidative damage and degradation of essential nutrients in the oil.
- Soybean is another popular crop used for its high protein and oil content. The ideal hot pressing temperature for soybeans is between 100-115 degrees Celsius (212-239 degrees Fahrenheit). At this temperature range, maximum oil yield can be achieved without compromising on quality or nutrient content. Higher temperatures can cause proteins in soybean oil to denature, resulting in a less desirable taste and aroma.
- Olive trees have been cultivated for centuries for their precious oils that are used in cooking and skincare products. Hot pressing olives at a temperature ranging from 25-35 degrees Celsius (77-95 degrees Fahrenheit) has been found to produce high-quality extra virgin olive oil with superior flavour profiles. However, recent studies have shown that increasing the hot pressing temperature up to 40 degrees Celsius (104 degrees Fahrenheit) can result in an increase in total phenolic compounds, known for their potent antioxidant properties, by up to 31%.
The hot pressing temperature has a significant impact on the extraction of oil from different types of crops. It is essential to understand the optimal temperature for each crop to achieve maximum yield without compromising on quality or nutrient content. Additionally, careful monitoring and control of duration and pressure during hot pressing are equally crucial in obtaining high-quality oils from our favourite crops.
Optimal Temperature Range for Maximum Oil Yield;
Finding the optimal temperature for hot pressing is crucial for maximising oil yield. Each crop has a specific range where extraction efficiency peaks. The oil yield of common crops such as sunflower, soybean, and canola varies significantly depending on factors like seed quality, extraction method, and growing conditions.
For instance, temperatures between 120°C to 160°C are often ideal for sunflower seeds. This range helps release oils without causing degradation of nutrients or flavour. On the other hand, soybeans tend to perform best at slightly lower temperatures, generally around 100°C to 130°C. This adjustment protects delicate compounds within the beans while still extracting ample oil. It’s essential not only to consider temperature but also the duration of exposure. Prolonged high heat can lead to undesirable results, including burnt flavours and reduced nutritional value.
Monitoring these variables closely during processing can make all the difference in your final product’s quality and quantity. Fine-tuning your approach will ensure you achieve that perfect balance every time.
Factors Affecting the Relationship between Temperature and Oil Yield;
When it comes to hot pressing temperature and its impact on oil yield in common crops, there are several factors that can influence this relationship. These factors have been extensively studied by researchers, and understanding them is crucial in maximising oil yield during the hot pressing process.
1. Type of Crop:
The type of crop being processed plays a significant role in determining the ideal hot pressing temperature for maximum oil yield. Different crops have different compositions and structures, which can affect how they respond to heat during the pressing process. For instance, some crops may require higher temperatures to release their oils, while others may reach their peak oil yield at lower temperatures.
2. Moisture
Various factors can influence the relationship between temperature and oil yield in common crops. In this section, we will discuss the key factors that play a significant role in determining the amount of oil extracted from hot pressing.
Other Considerations for Hot Pressing Techniques;
When it comes to hot pressing, several factors play a pivotal role beyond just temperature. The moisture content of the seeds is crucial. Too much moisture can lead to poor oil extraction, while too little may cause excessive heat and damage.
The type of press used also matters significantly. Different presses have varying efficiencies, which can impact yield and quality. Choosing the right equipment tailored for specific crops ensures optimal performance. Another consideration is seed preparation. Proper cleaning and conditioning enhance efficiency during hot pressing, leading to better yields.
Finally, monitoring the duration of pressing is essential. Overdoing it might result in undesirable flavours or even burnt oil, affecting overall quality greatly. Balancing these elements creates an environment conducive to maximising oil extraction success from various crops.
Conclusion:
Achieving the right balance between hot pressing temperature and oil yield is crucial for maximising extraction efficiency. Each crop has its unique characteristics, which means there’s no one-size-fits-all approach. Understanding how temperature affects oil quality and quantity can lead to better processing decisions.
Farmers and producers need to experiment within the established optimal ranges while considering factors like moisture content and seed variety. Continuous monitoring of these variables will aid in fine-tuning processes over time. Ultimately, striking a perfect balance can enhance profitability while maintaining quality standards in edible oils. By applying what we’ve learned about temperature effects on various crops, producers can improve their practices, leading to more sustainable outcomes in the long run.